# OpenCAPIF SDK

This repository develops a Python Software Development Kit(SDK) which focuses on connecting to OpenCAPIF (Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs) in a simple way, lowering integration complexity and allowing developers to focus on Network Applications (NetApps) or services development.
OpentCAPIF SDK provides a set of libraries to enable either CAPIF provider and invoker roles, and other functions to simplify procedures calls towards OpenCAPIF entity.
Current version of OpenCAPIF SDK is compatible with following publicly available releases:
- [OpenCAPIF Release 1.0](https://ocf.etsi.org/documentation/v1.0.0-release/)
# Table of Contents
1. [NetApp developers](#netapp-developers)
2. [OpenCAPIF SDK summary](#opencapif-sdk-summary)
3. [OpenCAPIF SDK requirements](#opencapif-sdk-requirements)
4. [NetApp developer path](#netapp-developer-path)
5. [OpenCAPIF SDK Configuration](./doc/sdk-configuration.md)
6. [OpenCAPIF SDK Usage](./doc/sdk-usage.md)
7. [OpenCAPIF SDK known issues](./doc/sdk-issues.md)
8. [OpenCAPIF SDK Developers](./doc/sdk-installation.md)
# NetApp developers
In the scope of CAPIF, a NetApp (Network Application) refers to an external application or service that interacts with the 3GPP network via standardized APIs. These NetApps typically leverage the capabilities and services provided by the underlying mobile network infrastructure, such as network slicing, quality of service (QoS), or location services.
NetApps can be developed by third-party service providers, network operators, or other stakeholders to offer a wide range of services, including enhanced communication features, IoT solutions, or content delivery, and they use CAPIF as the unified framework for securely discovering, accessing, and utilizing 3GPP network APIs.
For that purpose NetApps play 2 different roles when interacting with CAPIF:
- **Invoker**: a NetApp acting as an Invoker is responsible for consuming APIs exposed by other services. This role represents an external application or service that calls the 3GPP northbound APIs to utilize the network’s functionalities.
- **Provider**: a NetApp acting as a Provider is responsible for exposing its own APIs for use by Invokers. This role represents an entity that offers services through APIs, making them available to other external applications or Invokers.
**NetApps developers are the target users of OpenCAPIF SDK.**
## OpenCAPIF SDK summary
OpenCAPIF SDK brings a set of functions to integrate with the 5G Core's function CAPIF, as defined in [3GPP Technical Specification (TS) 29.222 V18.5.0 Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs](https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/129200_129299/129222/18.05.00_60/ts_129222v180500p.pdf). This section shows the mapping between the Python functions available in this SDK and the CAPIF OpenAPI APIs defined the reference standard:
| **3GPP CAPIF API** | **OpenCAPIF SDK function** | **Description** |
|-------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|
| /onboardedInvokers (POST) | onboard_invoker() | Registers a new invoker. |
| /onboardedInvokers/{onboardingId} (PUT) | update_invoker() | Updates an existing invoker for a specific `onboardingId`. |
| /onboardedInvokers/{onboardingId} (DELETE) | offboard_invoker() | Deletes an invoker for a specific `onboardingId`. |
| registrations (POST) | onboard_provider() | Registers a new service provider. |
| /registrations/{registrationId} (PUT) | update_provider() | Updates a service provider's registration for a specific `registrationId`. |
| /registrations/{registrationId} (DELETE) | offboard_provider() | Deletes a service provider's registration for a specific `registrationId`. |
| /allServiceAPIs (GET) | discover() | Retrieves a list of all available service APIs. |
| /trustedInvokers (PUT//POST) | discover() | Registers or updates trusted invokers. |
| /securities/{securityId}/token (GET) | get_tokens() | Retrieves a security token for a specific `securityId`. This JWT token is used to query the targeted services. |
| /{apfId}/service-apis(POST) | publish_services() | Registers a new service API into the system for a specific `apfId` |
| /{apfId}/service-apis/{serviceApiId} (DELETE) | unpublish_service() | Deletes a service API from the system for a specific `apfId`and `serviceApiId` |
| /{apfId}/service-apis/{serviceApiId} (PUT) | update_service() | Updates the details of an existing service API for a specific `apfId`and `serviceApiId` |
| /{apfId}/service-apis/{serviceApiId} (GET) | get_service() | Retrieves the details of a specific service API for a specific `apfId` and `serviceApiId` |
| /{apfId}/service-apis (GET) | get_all_services() | Retrieves a list of all available service APIs for a specific `apfId` |
NOTE: Above mentioned CAPIF APIs are defined in these 3GPP references:
- [CAPIF Invoker API specification](https://github.com/jdegre/5GC_APIs/blob/Rel-18/TS29222_CAPIF_API_Invoker_Management_API.yaml)
- [CAPIF Provider API specification](https://github.com/jdegre/5GC_APIs/blob/Rel-18/TS29222_CAPIF_API_Provider_Management_API.yaml)
- [CAPIF Discover API specification](https://github.com/jdegre/5GC_APIs/blob/Rel-18/TS29222_CAPIF_Discover_Service_API.yaml)
- [CAPIF Publish API specification](https://github.com/jdegre/5GC_APIs/blob/Rel-18/TS29222_CAPIF_Publish_Service_API.yaml)
- [CAPIF Security API specification](https://github.com/jdegre/5GC_APIs/blob/Rel-18/TS29222_CAPIF_Security_API.yaml)
## OpenCAPIF SDK requirements
In order to leverage OpenCAPIF SDK it is required to have registered a user in the target CAPIF instance, so contact administrator to have required predefined credentials (username and password).
# Netapp developer path
## Invoker NetApp
A NetApp development running as an Invoker would usually follow this process step by step making use of SDK:
1. **Create an Invoker object:** \
Initialize the invoker by creating an instance of the `CAPIFInvokerConnector` class, passing the required configuration file:
```python
invoker = CAPIFInvokerConnector(config_file=utilities.get_config_file())
```
2. **Onboard the Invoker**: \
Register the invoker with the CAPIF system to enable access to APIs:
```python
invoker.onboard_invoker()
```
3. **Create a Service Discoverer object:** \
Initialize the service discovery mechanism to search for available services:
```python
service_discoverer = ServiceDiscoverer(config_file=utilities.get_config_file())
```
4. **Discover available services:** \
Use the discover() method to retrieve a list of available APIs:
```python
service_discoverer.discover()
```
5. **Retrieve security tokens:** \
Use the get_tokens() method to obtain the necessary tokens for authenticating API requests:
```python
invoker.get_tokens()
```
Then all information for using the available APIs would be at Capif_api_security_context_details.json
This file would be placed in the invoker_folder path, more specifically in the folder that corresponds of the capif_username used in the config_file.
Here is a sample of this Capif_api_security_context_details [file](./samples/capif_api_security_context_details-sample.json)
Here is a code sample of the implementation of this hole [functionality](./netapp-samples/netapp-invoker-sample/netapp-invoker.py)
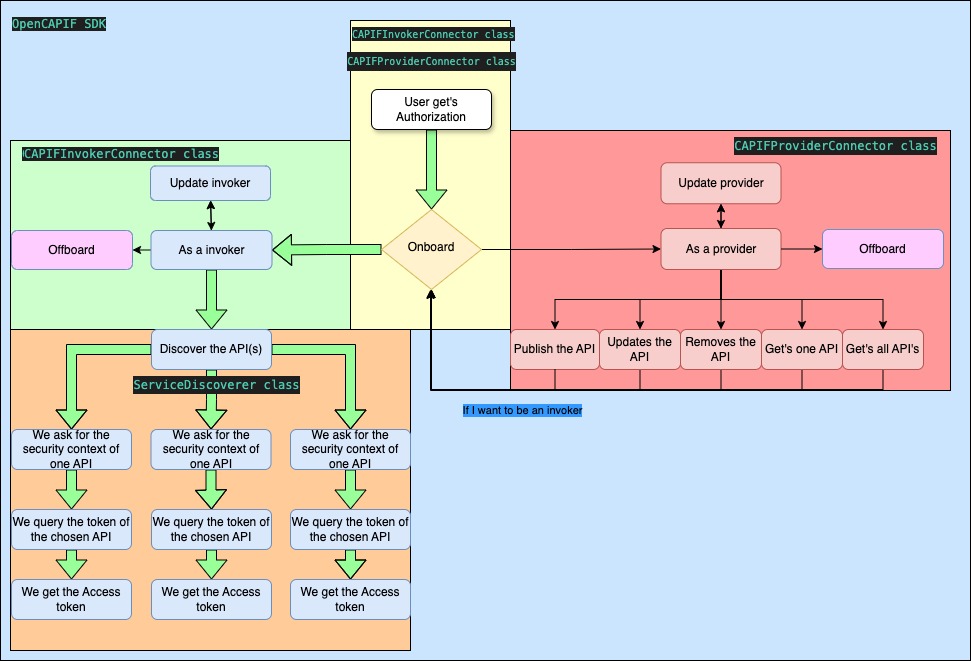
This image highlights Invoker path using SDK code:
### Important information for Invoker consumer
In the `invoker_folder`, it will be located several folders with each `capif_username` you have onboarded as a provider. For each folder, you could find:
- `Capif_api_security_context_details.json`: This file contains the information of your invoker. It will contain:
1. Your `api_invoker_id`.
2. If you have already used the Service Discovery Functionality, you will find all the available APIs with their information.
3. If you have already used the Service Get Token functionality, you will find your access token for using the APIs you have already discovered.
## Provider NetApp
A NetApp development running as a Provider would typically follow this process step by step, making use of the SDK:
1. **Create a Provider object:** \
Initialize the provider by creating an instance of the `CAPIFProviderConnector` class, passing the required configuration file:
```python
provider = CAPIFProviderConnector(config_file=utilities.get_config_file())
```
2. **Onboard the Provider:** \
Register the provider with the CAPIF system to enable the publication of APIs:
```python
provider.onboard_provider()
```
3. **Prepare API details:** \
Locate the provider API details in the provider_folder path, more specifically in the username folder. Choose the APF (Application Programming Function) and AEFs (Application Enabling Functions) identifiers, and fulfill the publish_req structure and the api_description_path:


4. **Publish the services:** \
Use the publish_services() method to register the APIs with the CAPIF framework(don't forget to update the CAPIFProviderConnector constructor in order to use the new APF and AEFs):
```python
provider = CAPIFProviderConnector(config_file=utilities.get_config_file())
provider.publish_services()
```
Here is a sample of the implementation of this hole [functionality](./netapp-samples/netapp-provider-sample/netapp-provider.py)
This image highlights Provider path using SDK code:

### Important information for Provider consumer
In the `provider_folder`, it will be located several folders with each `capif_username` you have onboarded as a provider, for each folder it is created by SDK this files:
- `Capif_provider_details.json` : Contains all the APFs and AEFs ids that have already onboarded with this capif_username
- `CAPIF_.json` : If it's already published or updated an API, It will be available a copy of your last payload.
- `Service_received.json` : If it's alread used the get an api or get all apis functionality, It will be available the response to your request.
- `Published-Apis.json` : Constains the currently published APIs with their ApiId


